Contents
BX2091 Tourism & Leisure Management: Demand and Sustainability
Q1. The Tourism System (15%)
1.1 Describe the extent to which Singapore functions simultaneously as an origin region, transit region and destination region. (5%, 100 words). (SLO1, SLO2 &CLO1)
1.2 Discuss the potential synergies and conflicts that emerge from each of the three
region combinations (e.g. origin/transit, origin/destination, transit/destination). (5%, 100 words). (SLO2, SLO3 & CLO3)
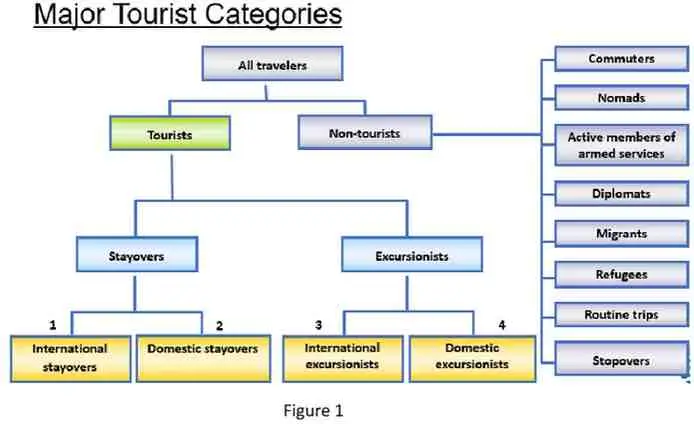
1.3 Define your most recent experience as a tourist, in terms of which of the four
categories in Figure 1 below it falls under, and also which purpose or purposes as
discussed in topic of purposive component of the tourist (e.g. leisure, VFR, business, sport, spiritual & health, education, others). (5%, 100 words). (SLO1 & CLO1)
Q2. Tourism Demand (20%)
2.1 Rank the following ten destination countries beginning with the one that you would most like to visit for a one-month vacation, and ending with the one that
you would be least interested in visiting for a one-month vacation. (3%). (SLO2 & CLO1).
Zimbabwe Fiji Mexico China United States France Dubai India United Kingdom Russia
2.2 Indicate the reasons for your rankings, referring in each case to each of the pull
factors discussed in class. (6%, 150 words). (SLO2 & CLO3)
2.3 Figures 2 and 3 below show the top tourist arrivals to Singapore in 2014 and 2024 respectively. Describe the differences between the two years, listing the factors that could possibly explain the differences. (6%, 150 words). (SLO1, SLO2 & CLO6)
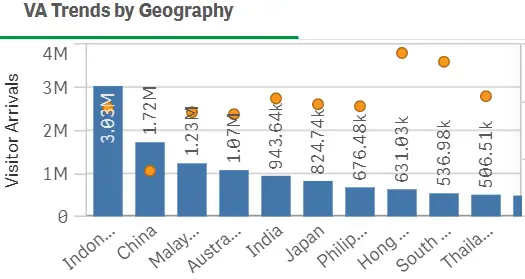
Figure 2 (2014 visitor arrivals to Singapore)
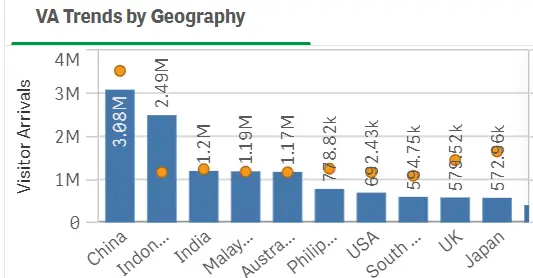
Figure 3 (2024 visitor arrivals to Singapore)
2.4 Predict what the pattern might look like in 2030. (5%,100 words). (SLO4 &
CLO6)
Q3. Tourism And Leisure Sustainability (20%)
3.1 Speculate on the likely positive socio-cultural, economic and environmental impacts associated with sex tourism (for example, in Bangkok’s red-light district).
(10%, 200 words). (SLO2, SLO3, CLO1 & CLO2)
3.2 Consider the likely negative socio-cultural, economic and environmental impacts
associated with volunteer tourism (for example, a scenario involving a volunteer organization with a humanitarian focus). (10%, 200 words). (SLO3 & CLO6)
Q4. Tourism And Leisure Marketing (25%)
4.1 Conduct a SWOT analysis of a particular destination. Each of the four destinations should be located adjacent to one another either at the international scale (e.g. Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia and Thailand) or at the subnational scale (e.g. Melaka, Kuala Lumpur, Genting Highlands, Kuantan). (14%, 250 words). (SLO2, SLO4 & CLO3)
4.2 Show how the other three destinations fit into the SWOT analysis of each destination (6%, 150 words). (SLO2, SLO4 & CLO3)
4.3 Indicate ways in which the competition-related threats of these other destinations can be converted into opportunities. (5%, 100 words). (SLO2, SLO4 & CLO6)
Q5. Tourism Demand (20%)
5.1 Select a mature destination. Identify the measures taken by the destination managers and communities to rejuvenate the destination. (10%, 200 words). (SLO2, SLO4 &
CLO3)
5.2 Show how these measures are innovative with respect to, for example, organization, collaboration, technology, product development, marketing and/or management. (10%,200 words). (SLO2 &CLO1)
Expert Answers on Above Tourism Management Questions
Singapore as origin, transit destination
An analysis of the Singaporean economy indicates that Singapore has significant strategic advantages in terms of its location which facilitates the opportunity to act simultaneously as an origin, transit and destination region. Its global connectivity along with strong travel culture further adds towards Singapore being preferred as a destination. As an origin region, the people living in Singapore have strong purchasing power which helps in generating outbound tourism, overseas leisure and business travel. As a transit region, the Changi airport in Singapore connects it with long overhaul routes between Asia, Europe and Oceania. As a destination, Singapore is known for attracting tourists by offering multicultural attractions, events, cuisine etc. The country therefore effectively plays all the three roles which strengthens its competitiveness in global tourism.
Synergies and conflict between region roles
The synergy occurs between origin and transit when changing Airport is used as a preferred hub by outbound Singaporeans. Synergy in case of origin and destination occurs when the travel patterns encourage reciprocal tourism flows and transit destinations synergy takes place when the transit visitors can be converted into stopover tourists.
Personal tourist experience
My own tourist experience falls under long term International leisure travel as my primary purpose of travelling to Singapore was to witness its sightseeing, food exploration and for leisure purposes.
Tourism demand
In terms of tourism demand, the most favourite location is France followed by the United Kingdom, Fiji, Mexico, United States and the least preferred is Zimbabwe.
Reasons based on pull factor
France and the UK ranks highest mainly because of strong cultural factors whereas Fiji is selected for natural attractions. The United States appeals for urban attraction while Zimbabwe has Limited accessibility and weaker tourism infrastructure. Difference between 2014 and 2024 arrivals
In 2014, it was mainly the visitors from Asian countries that visited Singapore but in 2024, it was the period after Covid and the Travellers from India visited the most because of rising income levels. Tourists from distant locations like Europe and the US have also increased overtime.
Prediction for 2030
By 2030, it is predicted that the tourists from China, India and Australia will arrive in abundance because of improved connectivity, technology enabling travel etc.
Tourism and Leisure sustainability
Positive impact of sex tourism: The positive impacts include diversity in urban nightlife, increased flow of tourists, significant employment, and benefits to supporting businesses.
Negative impact of volunteer tourism: It can lead to socio-cultural issues and the possibility that volunteers may have diverse resources towards volunteer oriented experiences rather than sustainable development.
| This model answer is reviewed by Pamela Lim, specialises in analysing business operations, undertaking strategic planning and more. Disclaimer: This answer is a model for study and reference purposes only. Please do not submit it as your own work. |
Want a Full Worked Out Answer with References?
Tourism and sustainability management tasks require a good amount of research and application of theories for better results. If you are faced with issues or challenges in completing your tourism and sustainability management task, consider taking help from Professional service providers like Singapore assignment help and remain ahead in your sustainability and tourism management assignment.
Related answers
Food Security, Climate Change & Singapore SDGs
CSR & Sustainability Strategy Evaluation: Case Study Analysis
Businesses Driving Sustainability and Innovation
Chew’s Agriculture: Sustainable Egg Production Case Study
FinTech & ESG in Carbon Markets — Project Brief
Sustainability & Global Business: Stakeholder Analysis
Sustainability Challenges in the Global Cocoa Sector